例程讲解-09-linear_regression_fast 快速线性回归(巡线)
视频教程20 - 巡线小车:https://singtown.com/learn/50037/
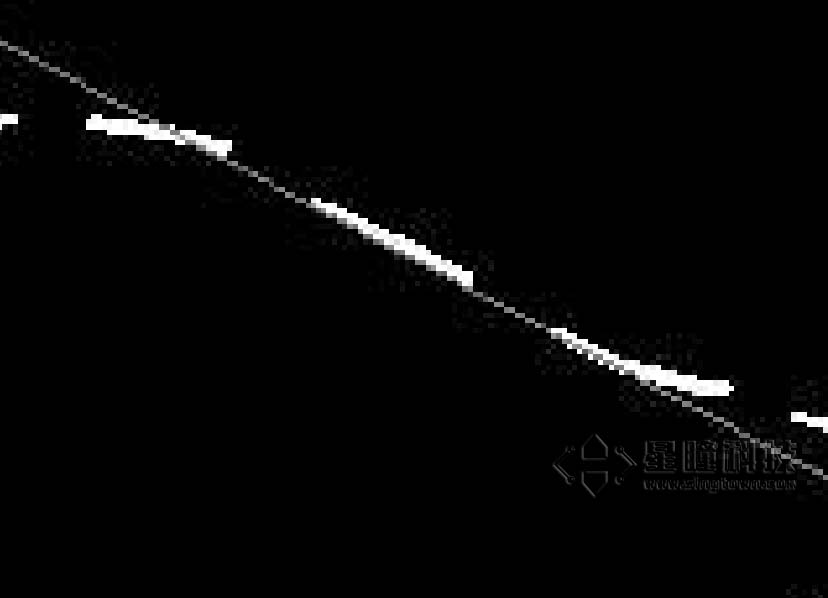
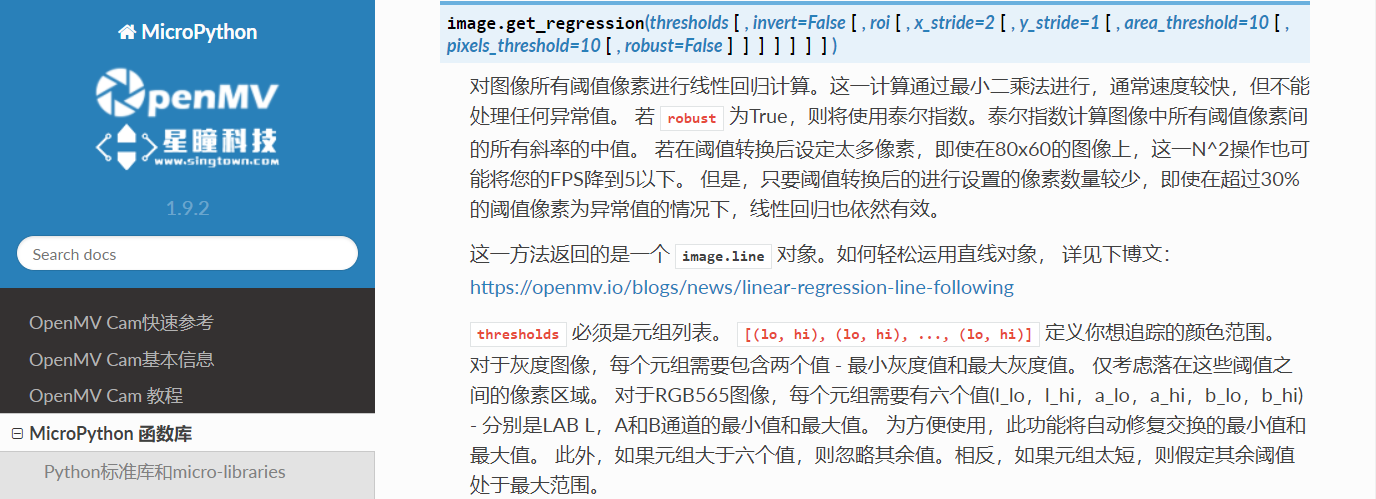
这个例子展示了在OpenMV Cam上使用get_regression()方法获得ROI的线性回归。使用这种方法,可以轻松让机器人跟踪所有指向相同大致方向的线。
本例程可以用于机器人巡线,效果非常好。
# 快速线性回归(巡线)例程
#
# 这个例子展示了如何在OpenMV Cam上使用get_regression()方法来获得
# ROI的线性回归。 使用这种方法,你可以轻松地建立一个机器人,它可以
# 跟踪所有指向相同的总方向但实际上没有连接的线。 在线路上使用
# find_blobs(),以便更好地过滤选项和控制。
#
# 这被称为快速线性回归,因为我们使用最小二乘法来拟合线。然而,这种方法
# 对于任何具有很多(或者甚至是任何)异常点的图像都是不好的,
# 这会破坏线条拟合.
#设置阈值,(0,100)检测黑色线
THRESHOLD = (0, 100) # Grayscale threshold for dark things...
#设置是否使用img.binary()函数进行图像分割
BINARY_VISIBLE = True # Does binary first so you can see what the linear regression
# is being run on... might lower FPS though.
import sensor, image, time
sensor.reset()
sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.GRAYSCALE)
sensor.set_framesize(sensor.QQVGA)
sensor.skip_frames(time = 2000)
clock = time.clock()
while(True):
clock.tick()
img = sensor.snapshot().binary([THRESHOLD]) if BINARY_VISIBLE else sensor.snapshot()
# Returns a line object similar to line objects returned by find_lines() and
# find_line_segments(). You have x1(), y1(), x2(), y2(), length(),
# theta() (rotation in degrees), rho(), and magnitude().
#
# magnitude() represents how well the linear regression worked. It goes from
# (0, INF] where 0 is returned for a circle. The more linear the
# scene is the higher the magnitude.
#函数返回回归后的线段对象line,有x1(), y1(), x2(), y2(), length(), theta(), rho(), magnitude()参数。
#x1 y1 x2 y2分别代表线段的两个顶点坐标,length是线段长度,theta是线段的角度。
#magnitude表示线性回归的效果,它是(0,+∞)范围内的一个数字,其中0代表一个圆。如果场景线性回归的越好,这个值越大。
line = img.get_regression([(255,255) if BINARY_VISIBLE else THRESHOLD])
if (line): img.draw_line(line.line(), color = 127)
print("FPS %f, mag = %s" % (clock.fps(), str(line.magnitude()) if (line) else "N/A"))
# About negative rho values:
#
# A [theta+0:-rho] tuple is the same as [theta+180:+rho].
如果要制作巡线小车的话,只需利用本程序得到的line对象的theta返回值,(theta代表返回线段的角度),利用theta来控制小车角度即可。
原图: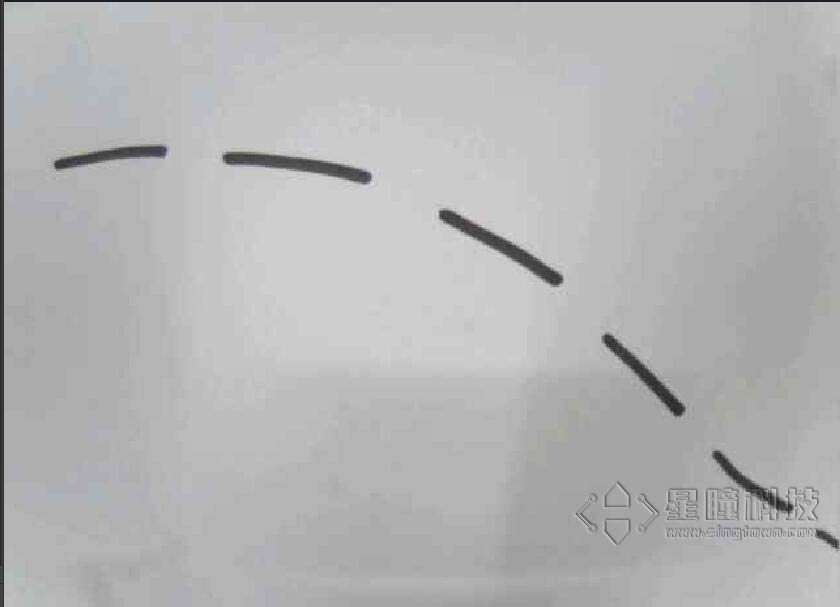
运行效果图: